In March 1951, Ruth Gmeiner, a United Press Staff writer, published a story about the growing problem of teenage drug addiction. Officials described heroin use as a “contagious disease.” A federal grand jury in Detroit reported they had uncovered shocking conditions . . . “Young people ranging in age between 14 and 21 have become confirmed and inveterate users of heroin.” Every big city noticed an uptick in the number of juveniles arrested on drug charges.

In Los Angeles, Robert Schoengarth started using heroin in 1948 as a student at North Hollywood Junior High School. He and a group of his friends grew marijuana in the Hollywood Hills. They weren’t entrepreneurs, they were pot philanthropists. What they didn’t consume themselves, they gave away to friends.
Raise your hand if you made stupid choices at 14. Yeah. Me too. Fortunately, my choices didn’t have lifelong consequences.
Late Wednesday evening, January 14, 1953, Morris Friedman worked behind the counter at his liquor store at 4100 Magnolia in Burbank. A dark-haired young man entered the store, bought a pack of cigarettes, and left. Moments later, he returned. He had a .22 in his pocket. He gestured at Friedman, “I want your money, sir.”
Friedman didn’t argue. He opened the cash register, grabbed a handful of bills, and handed them over. But the crook saw a few other bills in the drawer. He reached for them. Friedman grabbed the man’s arm, but the bandit pulled away and ran. The bandit was Robert.
Robert ran five blocks to his home. He replaced the gun, which belonged to his twin, William, in a dresser drawer. Passing through the living room where his father, Frank, spoke with a neighbor, he went into the front yard.
He called Frank from the house into the yard. “I told him I robbed the store.” It wasn’t Robert’s first brush with the law. Police arrested him twice before. Once for marijuana, and later for heroin. He spent time in the Los Angeles County Jail, and a California Youth Authority facility. He told his dad he’d been clean since his release. Frank didn’t believe him.
Robert said he couldn’t understand why he committed the robbery. He had a good job, making more than $62 a week as a mechanic’s apprentice. When Frank asked him for the stolen money, he gave it to him.
While Robert waited at home with his mother, Louise, for the police to arrive, Frank went to the liquor store and returned $33 to Friedman.
Patrolmen Ray Webb and Joe Mooney took Robert into custody. “I don’t know what’s wrong with me,” Robert said. “I suppose I have always been hanging around with the wrong crowd. That’s how I started using dope. Maybe they can put me in a hospital. Maybe it’d help me.”
Robert’s pain is palpable. So is Frank’s. Frank explained his actions by saying he wanted to help Robert, and that he feared that Robert’s twin brother, William, an aircraft worker, might be wrongly accused.
In desperation, Frank reached out to the well-known newspaperwoman, Florabel Muir. He spoke to her about Robert. “He really isn’t a bad boy. He started getting into bad company when he was in junior high school. It was then he started smoking marijuana. I didn’t know about it until he was arrested.”

Robert’s incarcerations did him no good. Frank said, “He’s only got worse with each sentence. I asked him the other night what in the world had happened to him and where he got the idea of taking a gun and sticking up somebody for money. He looked at me, sneered, and answered, ‘In jail. What do you think?’”
Back home for only a month, Robert seemed to do well. Then he asked to borrow $10. Frank couldn’t figure out why Robert would be broke right after payday—unless he was using drugs again. Robert denied it.
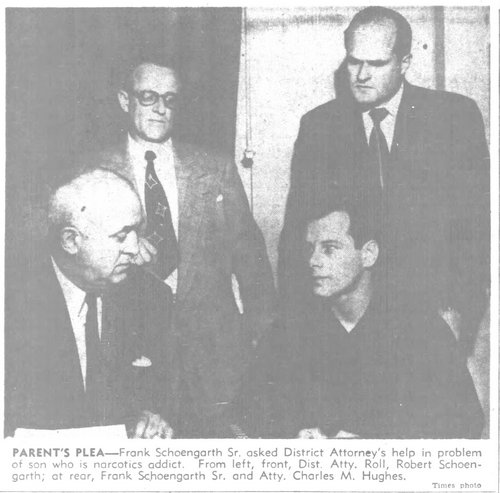
Frank hoped they wouldn’t return Robert to jail. He wanted him to go to a hospital for treatment. That would be up to the court. District Attorney Ernest Roll ordered a full investigation of Robert’s story. Robert told him he would “like to kick the habit if I got the chance.” He told Roll about his “graduation” from marijuana to heroin. The D.A. learned how easy it was for Robert to get high in a California Youth Camp. A friend supplied heroin through the mail.

In judge Charles Fricke’s court, Robert pleaded guilty to one count of first-degree robbery. The judge said he would place Robert in one of the California Youth Authority institutions for another chance at sobriety.
In less than two years, Robert was out of CYA and back in the news.
Police arrested him and his brother William on dope charges in February 1955. With them was a 17-year-old girl. The twins had their own place at 11920 Riverside Drive in North Hollywood. Police found a hypodermic needle kit and two caps of heroin. The girl told officers she went with Robert downtown to Temple Street, where they scored a gram of heroin from a dealer for $15.
Maybe the evidence was insufficient for prosecution, because by October Robert was again under arrest for drugs.
Police booked Robert and 18-year-old Rosalyn Berman after stopping their car on Emelita Street and Lankershim Boulevard. Robert drove erratically, and police noticed Rosalyn drop a packet from the car. Both had fresh needle marks on their arms and appeared to be under the influence.
Only 20-years-old, and Robert’s life was circling the drain.
Even after six years of addiction and legal woes, Robert was young enough to change the course of his life. Could he do it?
NEXT TIME: Robert’s story continues.

 Ewing’s attorneys told reporters they were worried that their client had met with “foul play”. Both the police and the district attorney were convinced that Ewing’s convenient disappearance was a hoax.
Ewing’s attorneys told reporters they were worried that their client had met with “foul play”. Both the police and the district attorney were convinced that Ewing’s convenient disappearance was a hoax.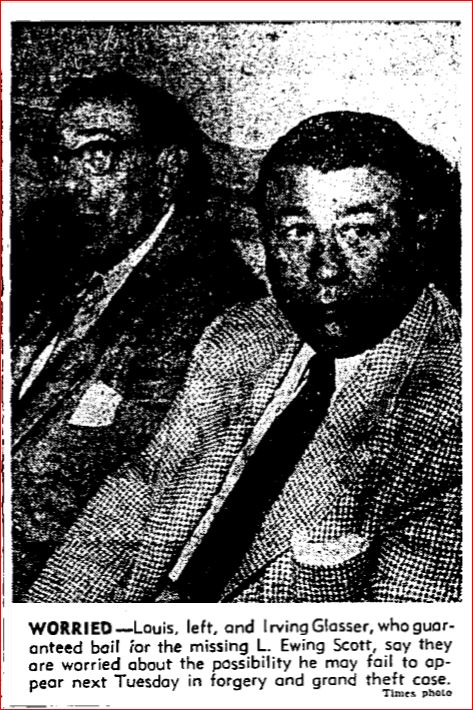 So, was Ewing sitting on a distant beach sipping a cocktail with a colorful little umbrella in it; or was he dead and buried in an unmarked shallow grave along Angelus Crest Highway? Nobody knew for sure.
So, was Ewing sitting on a distant beach sipping a cocktail with a colorful little umbrella in it; or was he dead and buried in an unmarked shallow grave along Angelus Crest Highway? Nobody knew for sure.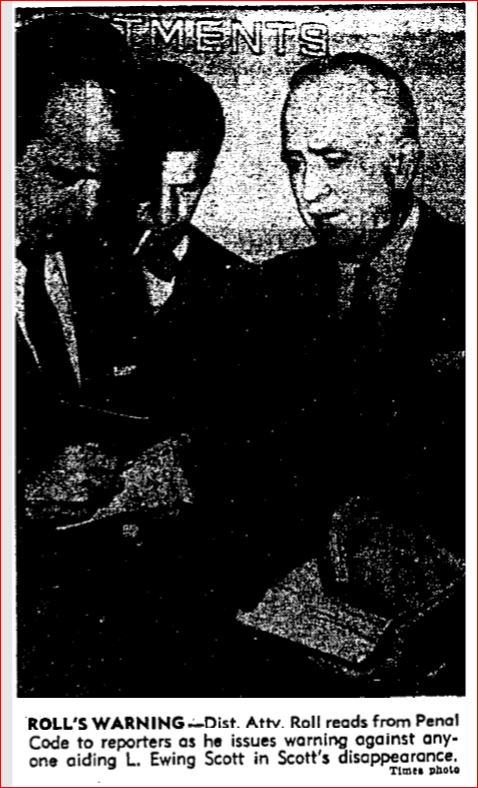
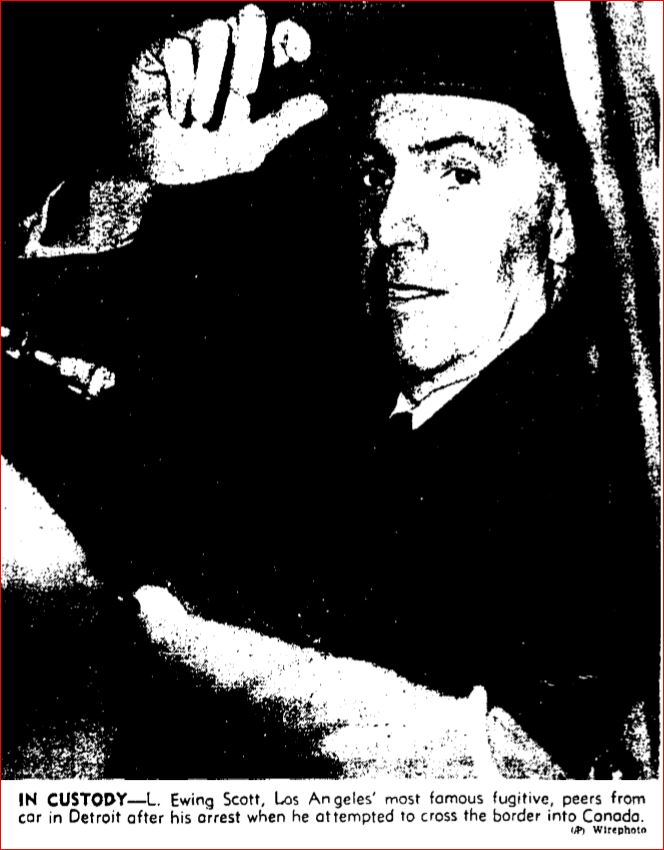
 Ewing was charming and friendly during his interview until a reporter asked him point-blank if he had murdered his wife. Scott replied, “That is an asinine question. It is just plain ridiculous and stupid. It is the last thing I would want to do.”
Ewing was charming and friendly during his interview until a reporter asked him point-blank if he had murdered his wife. Scott replied, “That is an asinine question. It is just plain ridiculous and stupid. It is the last thing I would want to do.” As far as any possible film, the charming, sophisticated and good looking English actor, Ronald Colman, seemed to Ewing to be the obvious choice to portray him on the big screen. Who would play Evelyn? Ewing wasn’t so sure. “As far as Mrs. Scott goes, I don’t know who would be exactly right. perhaps an older Peggy Lee, or Mary Astor. I’d have to see the woman first.” After further thought, Ewing said about the as yet unnamed actress, “I do know that she’ll have to be smart, dignified and rather good looking–and definitely not the wisecracking type.” Okay. I guess Joan Blondell wouldn’t be considered — although personally I think she would have been a fantastic choice.
As far as any possible film, the charming, sophisticated and good looking English actor, Ronald Colman, seemed to Ewing to be the obvious choice to portray him on the big screen. Who would play Evelyn? Ewing wasn’t so sure. “As far as Mrs. Scott goes, I don’t know who would be exactly right. perhaps an older Peggy Lee, or Mary Astor. I’d have to see the woman first.” After further thought, Ewing said about the as yet unnamed actress, “I do know that she’ll have to be smart, dignified and rather good looking–and definitely not the wisecracking type.” Okay. I guess Joan Blondell wouldn’t be considered — although personally I think she would have been a fantastic choice.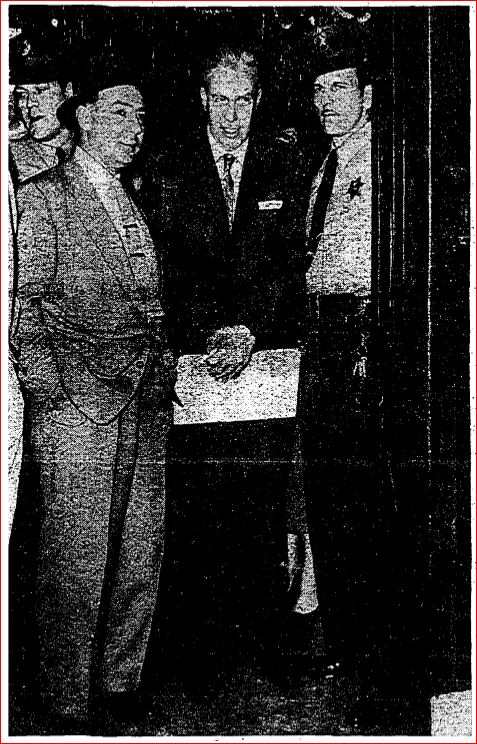 Despite the lack of a physical body, Deputy District Attorney J. Miller Leavy, was confident that the corpus delicti of murder could be established. There was a mountain of compelling circumstantial evidence to bolster the State’s case. Leavy was not only certain of a conviction, he asked for the death penalty.
Despite the lack of a physical body, Deputy District Attorney J. Miller Leavy, was confident that the corpus delicti of murder could be established. There was a mountain of compelling circumstantial evidence to bolster the State’s case. Leavy was not only certain of a conviction, he asked for the death penalty.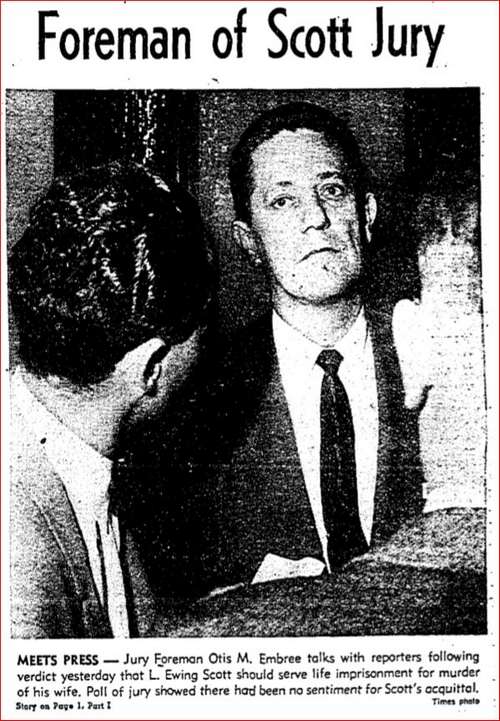 Several days later, following four hours of deliberation, the jury returned with their sentence: life in prison.
Several days later, following four hours of deliberation, the jury returned with their sentence: life in prison. Evelyn’s brother, Raymond, was satisfied with the outcome of the trustee battle — the bank was his nominee. Ewing’s attorneys were said to be plotting a new strategy to put him back in charge of the estimated $270,000 estate. But losing the trustee fight wasn’t Ewing’s most pressing problem. Rumors of a grand jury and possible indictments were looming large on the horizon.
Evelyn’s brother, Raymond, was satisfied with the outcome of the trustee battle — the bank was his nominee. Ewing’s attorneys were said to be plotting a new strategy to put him back in charge of the estimated $270,000 estate. But losing the trustee fight wasn’t Ewing’s most pressing problem. Rumors of a grand jury and possible indictments were looming large on the horizon. The grand jury indicted Ewing on 13 counts, 4 of theft and 9 of forgery. His constant companion was divorcee Marianne Beaman who seemed to have no problem consorting with a man who may have murdered his wife. Marianne even flatly refused to testify about out-of-town jaunts she and Ewing had taken. Her refusal to speak could lead to a contempt charge.
The grand jury indicted Ewing on 13 counts, 4 of theft and 9 of forgery. His constant companion was divorcee Marianne Beaman who seemed to have no problem consorting with a man who may have murdered his wife. Marianne even flatly refused to testify about out-of-town jaunts she and Ewing had taken. Her refusal to speak could lead to a contempt charge.